LAA OCCLUDER
STRUCTURAL INTERVENTIONS
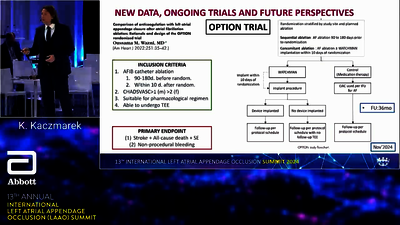
Designed to treat patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF), who are at risk of ischemic stroke, the Amplatzer™ Amulet™ LAA Occluder offers complete closure of the left atrial appendage (LAA) and immediately eliminates the need for oral anticoagulants (OACs).1
SWITCH TO THE REFERRAL VIEW For more information specific to neurology regarding LAA Occlusion
REDUCE THE RISK OF STROKE, ELIMINATE ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS
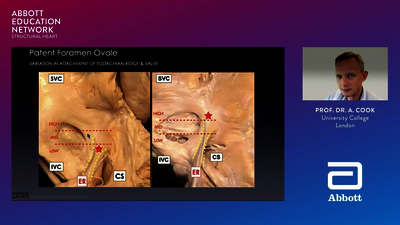
What is LAAO?
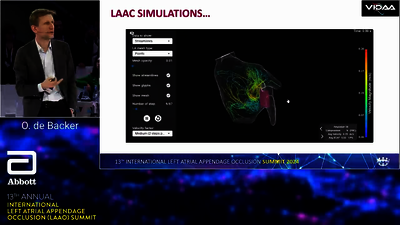
Left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) is a minimally invasive catheter-based therapy to close the left atrial appendage. The Amplatzer™ Amulet™ LAA Occluder provides complete closure, immediately eliminating the need for OACs.
For those patients who are either contraindicated for OACs or wish to discontinue use, LAAO is a viable option to reduce their risk of stroke.

Reducing stroke risk
David Hildick-Smith, MD, Royal Sussex County Hospital, Brighton, England
“What this therapy [use of the Amplatzer™ Amulet™ LAA Occluder] does for the patient is twofold. One, it physically deals with the problem and reduces the risk of stroke very substantially. But more than that, it also offers patients a peace of mind.”
TV
TV
- Amplatzer™ Amulet™ LAA Occluder Instructions for Use.
- Lakkireddy D, Thaler D, Ellis CR, et al. Amplatzer™ Amulet™ Left Atrial Appendage Occluder versus Watchman™ device for stroke prophylaxis (Amulet IDE): A randomized, controlled trial. Circulation. 2021; 144(19) :1543–1552. doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.057063.
- Suradi HS, Hijazi ZM. Left atrial appendage closure: outcomes and challenges. Neth Heart J. 2017;25:143–151. doi.org/10.1007/s12471-016-0929-0.
- Kakkar AK, Mueller I, Bassand J-P, et al. Risk profiles and antithrombotic treatment of patients newly diagnosed with atrial fibrillation at risk of stroke: perspectives from the international, observational, prospective GARFIELD registry. PLoS ONE. 2013; 8(5):e63479. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063479.
- Baman JR, Mansour M, Heist EK, et al. Percutaneous left atrial appendage occlusion in the prevention of stroke in atrial fibrillation: a systematic review. Heart Failure Rev. 2018;23:191–208. doi.org/10.1007/s10741-018-9681-4.
- European Heart Rhythm Association; European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery; Camm AJ, Kirchhof P, Lip GY, et al. Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2010;31(19):2369–429. doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehq278. Erratum in: Eur Heart J. 2011;32(9):1172. PMID: 20802247.