STROKE RISK FACTORS
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with a 5-fold increase in the risk of ischemic stroke.1 Left atrial appendage (LAA) closure reduces the risk of stroke in non-valvular AF patients (NVAF) who are seeking an alternative to oral anticoagulants.2,3
SWITCH TO THE interventional VIEW For more information specific to interventional cardiology regarding LAA Occlusion
AF AND THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE
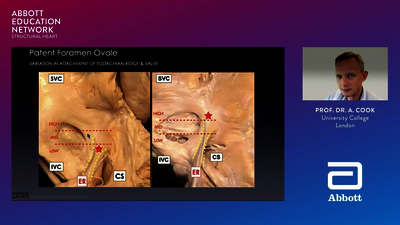
Because the upper chambers of the heart (atria) are unable to contract properly in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF), clots are able to form. A common site for clot formation is the left atrial appendage (LAA), which is attached to the left atrium. More than 90% of strokes in people with non-valvular AF (NVAF) are caused by blood clots formed in the LAA.4,5
FIND OUT MORE:
AF AND THE CHALLENGES OF MEDICATION
Many patients at risk of stroke want an alternative to oral anticoagulants (OACs), for example, warfarin and non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants (NOACs).6


CHALLENGES OF NOACS AND WARFARIN INCLUDE:6,8
- Significant bleeding risks
- Significant non-compliance rates
- Regular international normalized ratio (INR) monitoring (warfarin)
- Food and drug interaction issues (warfarin)
- Complicates surgical procedures
- High cost (NOACs)
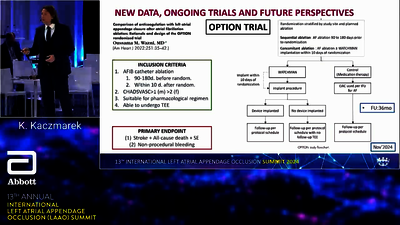
LAA OCCLUSION IS AN ALTERNATIVE TO LONG-TERM MEDICATION FOR REDUCING RISK OF STROKE
Surgery to remove or tie off the LAA is highly invasive.
- Typically reserved for patients undergoing cardiac surgery for concomitant conditions
- Complete closure rates range from 0% to 100%6
Transcatheter occlusion of the LAA is minimally invasive.
- Closure rates are 98.9% with the Amplatzer™ Amulet™ LAA Occluder2,3
TV
TV
- Amplatzer™ Amulet™ LAA Occluder Instructions for Use.
- Lakkireddy D, Thaler D, Ellis CR, et al. Amplatzer Amulet Left Atrial Appendage Occluder versus Watchman device for stroke prophylaxis (Amulet IDE): A randomized controlled trial. Circulation. 2021; 144(19):1543–1552. doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.057063.
- Suradi HS, Hijazi ZM. Left atrial appendage closure: outcomes and challenges. Neth Heart J. 2017;25(2):143–151. doi.org/10.1007/s12471-016-0929-0.
- Kakkar AK, Mueller I, Bassand JP, et al. Risk profiles and antithrombotic treatment of patients newly diagnosed with atrial fibrillation at risk of stroke: perspectives from the international, observational, prospective GARFIELD registry. PLOS ONE. 2013;8(5):e63479. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063479.
- Baman JR, Mansour M, Heist EK, et al. Percutaneous left atrial appendage occlusion in the prevention of stroke in atrial fibrillation: a systematic review. Heart Fail Rev. 2018;23(2):191–208. doi.org/10.1007/s10741-018-9681-4.
- European Heart Rhythm Association; European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery; Camm AJ, Kirchhof P, Lip GY, et al. Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2010;31(19):2369–429. doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehq278. Erratum in: Eur Heart J. 2011;32(9):1172. PMID: 20802247.